Driving Next Generation Data Centers Toward 400G
Market Trend
How and why 400G networks are being used in the hyperscale data center As our data-centric world rapidly develops around us, the capacity of the networks that carry all the data traffic are constantly being stretched to their limits. The ever-increasing rise of more and more cloud applications and services, the expanding use of video in many applications, and a steady climb in the number of users all adds up to an unrelenting volume of data. With Hyperscale data center operators looking for solutions to the current traffic growth, they also have to cope with an upcoming traffic surge from new technologies. The advent of 5G mobile networks, the Internet of Things (IoT), edge computing, and AI machine learning and deep learning are all data intensive and are poised to cause a massive increase in network traffic.
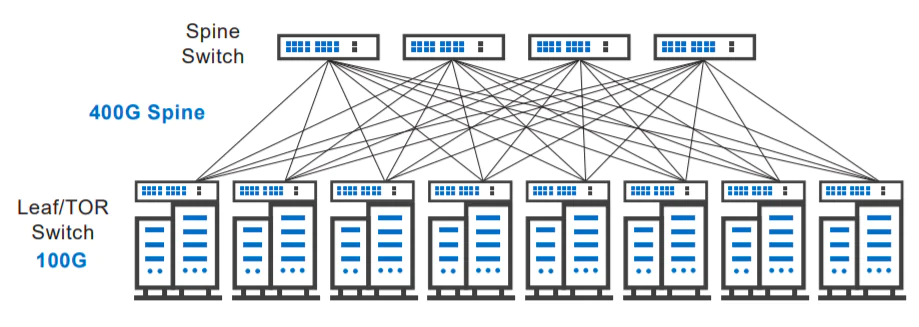
A typical hyperscale data center has seen storage increasing more than 50% annually for some years, with by far the bulk of data traffic being moved within the data center. Hyperscale data center operators are now looking to the next-generation 400G network infrastructure to help absorb the demanding workloads. With greater server density and processing power in the data center, operators need the higher-bandwidth 400G links to replace the limited 100G/200G connections. But, 400G offers operators much more than that. The new advanced 400G network equipment delivers greater efficiency, at a lower cost per bit, lower power, with potentially fewer points of failure in the network. As operators struggle to meet high-volume network demands, reduce operational costs and reach sustainability goals, 400G offers an ideal solution.
Open networking is helping to transform the way IT is deployed and used by many types of businesses. Open networks are based on networking hardware whose designs are fully open-sourced, with a choice of independent open soſtware for NOS, SDN, virtualization and cloud orchestration.
How and why 400G networks are being used in the hyperscale data center
For years, hyperscale data center operators have been enjoying the benefits of open networking: automated and accelerated provisioning of network capacity and services, greater control over the development of enhanced network services, flexibility to work with best-in-class suppliers, reduced network equipment expenses and reduced operating expenses. These open network benefits are now available for many more network use cases. Public and private cloud data centers of all sizes are being deployed with network fabrics built from open TOR and spine switches. Open networks are addressing telecommunications service provider requirements for new central office architectures, managed services delivery, monitoring and analytics networks, and Internet exchanges.
Now, the growth of IoT, AI and cloud computing machine learning has driven the requirement for higher processing speed and lower latency as well as high speed storage capability. All these demands require higher network bandwidth toward 400G or above.
A typical hyperscale data center has seen storage increasing more than 50% annually for some years, with by far the bulk of data traffic being moved within the data center. Hyperscale data center operators are now looking to the next-generation 400G network infrastructure to help absorb the demanding workloads. With greater server density and processing power in the data center, operators need the higher-bandwidth 400G links to replace the limited 100G/200G connections. But, 400G offers operators much more than that. The new advanced 400G network equipment delivers greater efficiency, at a lower cost per bit, lower power, with potentially fewer points of failure in the network. As operators struggle to meet high-volume network demands, reduce operational costs and reach sustainability goals, 400G offers an ideal solution.
Open networking is helping to transform the way IT is deployed and used by many types of businesses. Open networks are based on networking hardware whose designs are fully open-sourced, with a choice of independent open soſtware for NOS, SDN, virtualization and cloud orchestration.
How and why 400G networks are being used in the hyperscale data center
For years, hyperscale data center operators have been enjoying the benefits of open networking: automated and accelerated provisioning of network capacity and services, greater control over the development of enhanced network services, flexibility to work with best-in-class suppliers, reduced network equipment expenses and reduced operating expenses. These open network benefits are now available for many more network use cases. Public and private cloud data centers of all sizes are being deployed with network fabrics built from open TOR and spine switches. Open networks are addressing telecommunications service provider requirements for new central office architectures, managed services delivery, monitoring and analytics networks, and Internet exchanges.
Now, the growth of IoT, AI and cloud computing machine learning has driven the requirement for higher processing speed and lower latency as well as high speed storage capability. All these demands require higher network bandwidth toward 400G or above.
Leaf and Spine Topology for Data Center